Psoriasis – an auto-immune disorder
By Dr Raya Grishina-Gunn
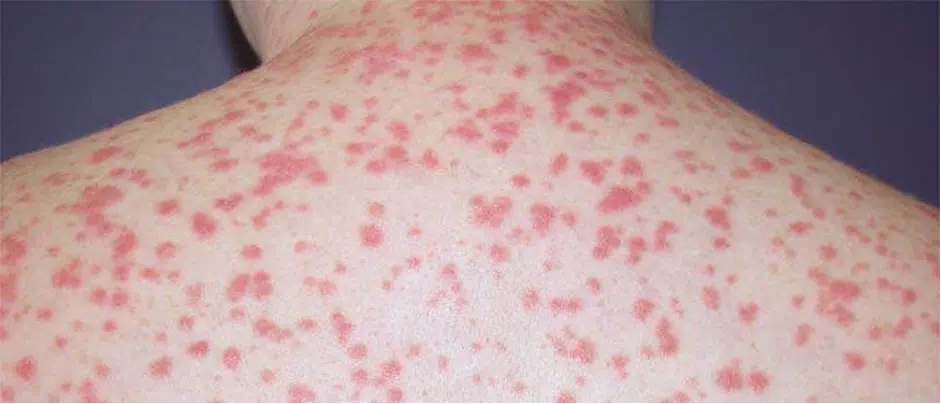
Psoriasis is an auto-immune disorder which is characterized by distinctive lesions. These typically start as red and scaling papules that then merge to oval plaques. These plaques can be small or wide spread. The scale can become extremely thick, especially on the sculp.
Whilst it can occur at ANY age the 2 most common age brackets are:
- 15 to 25 years of age
- 50 to 60 years of age
Psoriasis is caused by:
- Genetic factors
- Multiple genes
- Family history
- Environmental factor
- Infections
- Injuries
- Obesity
Compared to the general population patients with Psoriasis are at a higher risk of other conditions.
- Other autoimmune conditions:
- Ulcerative colitis and
- Crohn’s disease
- These are 3.8 to 7.5 more likely in people with Psoriasis
- Cardiovascular disease
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Hyperlipidemia
- Obesity
- Metabolic syndrome
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Lower Vitamin D levels especially in those who have BMI greater than 27
- Depression and Anxiety – the prevalence is as high as 60%
- Poor self-esteem
- Sexual dysfunction
- Increased use of alcohol and/or smoking
- Poor quality of life.
Psoriasis erodes self-image, and forces people into a life of concealment and self-consciousness. People tend to avoid social activities including being in the sun, which is not helpful as it is the very activity that can help clear the disease. Even if patients have only a few plaques, Psoriasis appears to others more serious than it actually is – psychological effects must always be considered.
The presence of other disorders (or diseases) in addition to the Psoriasis (Comorbidities) tend to increase with age, so nearly half of patients with Psoriasis aged over 65 have at least 3 comorbidities. There are different types of Psoriasis:
- Plaque
- Guttate
- Erythrodermic
- Flexural
Treatment:
There are a number of therapies.
Locally applied therapies (Topical Therapies):
- Steroid creams,
- Calcipotriol
- Coal Tar
Light therapy – A combination of Red & Blue light
- LED Red light helps to reduce inflammation
- LED Blue light helps to treat redness and the skin rash (Erythema)
- Treatment is usually a total of 8 to 10 sessions
- 2 sessions weekly.
- Since Psoriasis is a chronic condition, “Light Therapy” may need to be repeated during flare-ups.
Oral medications:
- Methotrexate
- Cyclosporine
- And others
New therapies:
Biologicals and immunotherapy
Most of the time Psoriasis is a mild disease and responds well to light therapy and medicines applied directly to the affected area. New therapies are also very effective and have been shown to be safe to use. It is very important to treat associated conditions as they DECREASE the severity of Psoriasis. Prevention of the following will decrease the onset of Psoriasis
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Diabetes,
- Hypertension
- Obesity
Lifestyle medicine interventions that include the following can
Improve symptoms, prevent recurrence, Decrease duration and the burden of this condition
- Targeting treatment of any triggering infections early,
- Reducing smoking
- Reducing alcohol
- Weight loss
- Stress management and
- Management of other disorders (or diseases) (co-morbidities).
Speak to your doctor to help prevent, treat and reduce recurrence of this disease.




Recent Comments